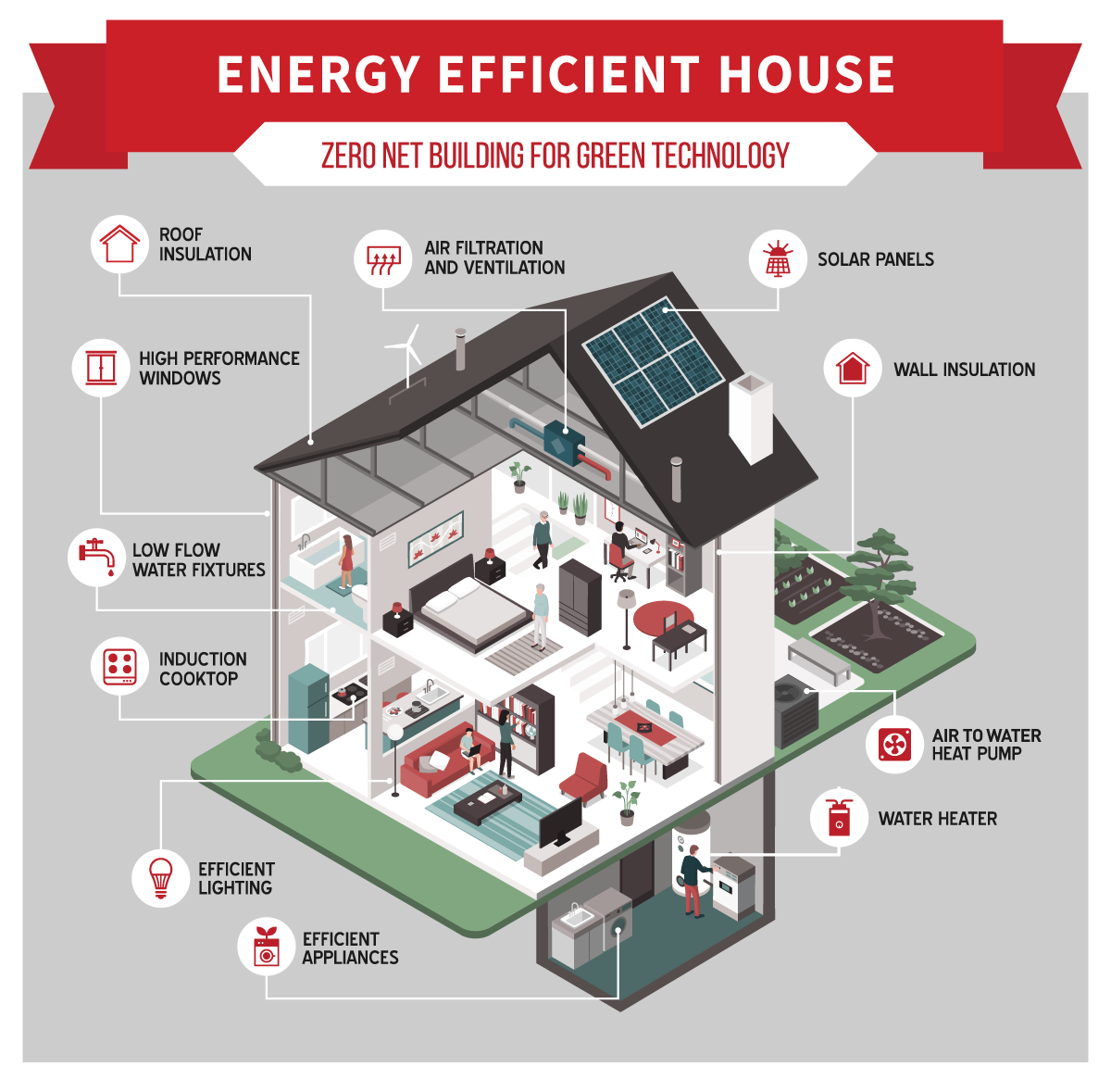
Benefits of a Hydronic Radiant System

Recently there has been a great deal interest in all electric hydronic heated homes across the country, spurred by California’s commitment to all electric homes powered by renewable electricity and now being discussed and built across the country. The collapse of solar electric panel and storage costs and the rise of superefficient heat pumps make this possible and cost effective.
The goal is to provide a building design with integrated highly efficient electric heating, hot water and cooling solution whose electric demand is low enough for a solar electric system to meet the entire load (and fit the roof).
Air-to-air forced air super-efficient mini split systems with a separate electric hot water heat pump have been available for some time now. Similar solutions are now available for hydronic systems that include hot water supply without the sound, lower efficiency and space demands of standalone heat pump water heaters, or the visual impact of wall mounted mini split terminal units.